Convert Julian Date To Gregorian
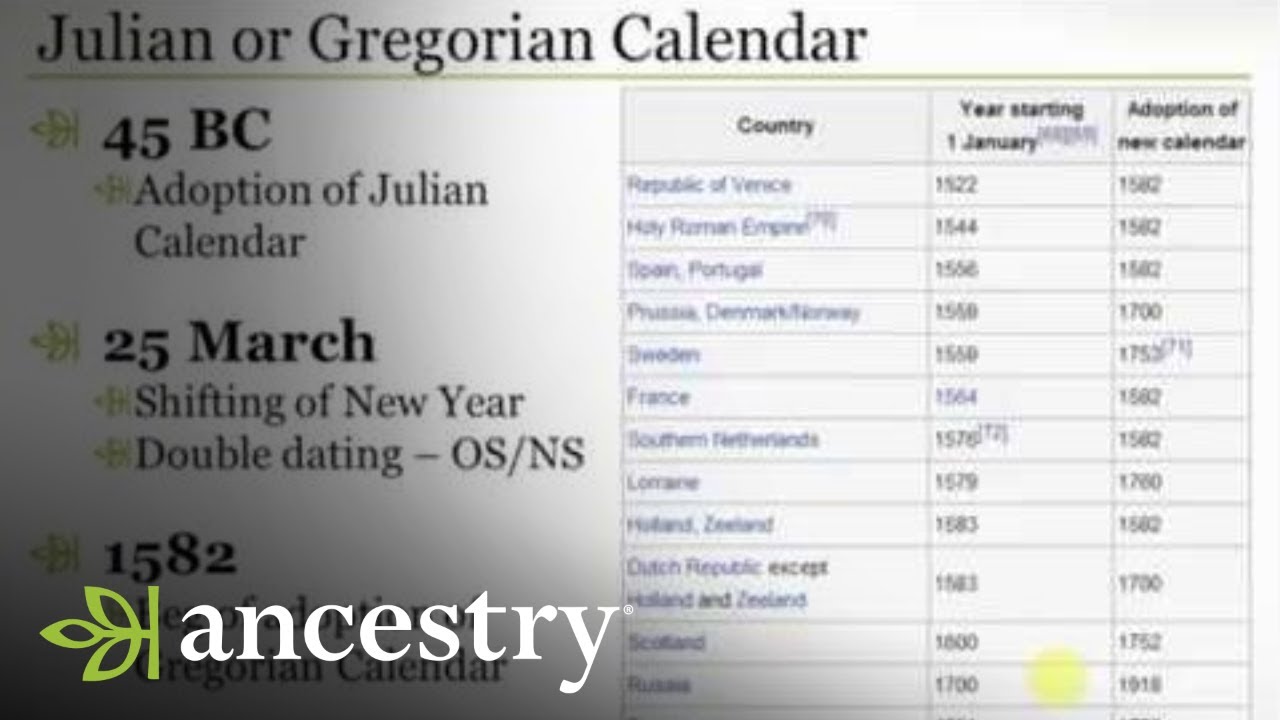
Convert to and from the Hebrew, Gregorian and Julian Calendars. Enter a date in any of the boxes below and press the 'Calculate' button to show that date in all of the other calendars. Please remember that in the Hebrew calendar, any Gregorian date you calculate, after sundown, belongs to the next Jewish day. To get a Gregorian date, you join the F00365 table using the ONDTEJ field (which is the Julian date),and you return the ONDATE value, which is Gregorian. SELECT DateReq.ONDATE FROM F00101 NamesData INNER JOIN F00365 DateReq ON DateReq.ONDTEJ = NamesData.ABUPMJ No math required. No weird issues with leap years. . Gregorian calendar. Julian calendar. The calendar eras. The Muslim calendar. The Gregorian calendar conversion. Julian and Gregorian calendars. Days between dates. The historical version. Hebrew calendar. Date and Time section ( 55 calculators ).
The Julian Day Count is a uniform count of days from aremote epoch in the past (-4712 January 1, 12 hours Greenwich Mean Time(Julian proleptic Calendar) = 4713 BCE January 1, 12 hours GMT (Julian prolepticCalendar) = 4714 BCE November 24, 12 hours GMT (Gregorian proleptic Calendar)).At this instant, the Julian Day Number is 0. It is convenient for astronomersto use since it is not necessary to worry about odd numbers of days in amonth, leap years, etc. Once you have the Julian Day Number of a particulardate in history, it is easy to calculate time elapsed between it and anyother Julian Day Number.
The Julian Day Count has nothing to do with the Julian Calendar introducedby Julius Caesar. It is named for Julius Scaliger, the father of JosephusJustus Scaliger, who invented the concept. It can also be thought of asa logical follow-on to the old Egyptian civil calendar, which also usedyears of constant lengths.
Scaliger chose the particular date in the remote past because it was beforerecorded history and because in that year, three important cycles coincidedwith their first year of the cycle: The 19-year Metonic Cycle, the 15-yearIndiction Cycle (a Roman Taxation Cycle) and the 28-year Solar Cycle (thelength of time for the old Julian Calendar to repeat exactly).
It is easy (with your calculator) to calculate the Julian Day Number ofany date given on the Gregorian Calendar. The Julian Day Number so calculatedwill be for 0 hours, GMT, on that date. Here's how to do it:
1) Express the date as Y M D, where Y is the year, M is the month number(Jan = 1, Feb = 2, etc.), and D is the day in the month.
2) If the month is January or February, subtract 1 from the year to geta new Y, and add 12 to the month to get a new M. (Thus, we are thinkingof January and February as being the 13th and 14th month of the previousyear).
3) Dropping the fractional part of all results of allmultiplicationsand divisions, let
This is the Julian Day Number for the beginning of the date in questionat 0 hours, Greenwich time. Note that this always gives you a half day extra.That is because the Julian Day begins at noon, Greenwich time. Thisis convenient for astronomers (who until recently only observed at night),but it is confusing.
Example: If the date is 1582 October 15,
To convert a Julian Day Number to a Gregorian date, assume that it isfor 0 hours, Greenwich time (so that it ends in 0.5). Do the following calculations,again dropping the fractional part of all multiplicatons and divisions.Note: This method will not give dates accurately on the Gregorian ProlepticCalendar, i.e., the calendar you get by extending the Gregorian calendarbackwards to years earlier than 1582. using the Gregorian leap year rules.In particular, the method fails if Y<400. Thanks to a correspondent, Bo Du, for some ideas that have improved this calculation.
Example: Check the first calculation by starting with JD = 2299160.5
Practice: Calculate the Julian Day Number for 0 hours GMT on thedate of your birthday. Check your result by calculating the date of yourbirthday from the Julian Day Number.
Remark: You can do the calculation of Julian Calendar Date-->JulianDay Number by ignoring the calculation of A and B, and setting C=0; to gofrom Julian Day Number to Julian Calendar Date, bypass the calculation ofW and X and simply set A=Z. These calculations are useful also when convertingbetween the Gregorian and Julian calendars (e.g., to correlate dates onthe Julian Calendar in England prior to 1752 with dates on the Gregoriancalendar). For example, to go from Gregorian to Julian calendar date, convertthe Gregorian date to Julian Day Number, then convert the Julian Day Numberto Julian calendar date. This method even works for dates prior to 1582and correctly gives years prior to the Common Era as negative years (withyear 0 corresponding to 1 BCE, year -1 corresponding to 2 BCE, etc.) However,it does not work with negative Julian Day Numbers and does notwork when going to the Gregorian calendar for years before 400 CE.
To assist you in practicing Julian Day Number conversions, I have made upa page that contains a Julian Day Number Calculator.You can put any date in the Common Era (that is, AD) into this calculator,and it will give you the Julian Day Number, on both the Julian Calendarand the Gregorian Calendars. Or, you can put in a Julian Day Number andit will compute the calendar date. Have fun!
 My home page is located here.
My home page is located here.This page Copyright (C) 1996-1998 by William H. Jefferys. All Rights Reserved.
Troubleshooting
Problem
Is there any way to translate a Julian date to a regular calendar (Gregorian) date in DecisionStream?
Resolving The Problem
Use the following calculation:
Select date (days(concat(cast(integer(1900000+'SDIVD') /1000 as Char(4)),'-01-01'))+mod(integer(1900000+' SDIVD'),1000)-1)
where SDIVD is the Julian date field.
This calculation breaks the Julian expression 99123 into 2 parts. The first part of the calculation creates the century date and adds the first day of the year, thus the 01-01. So it would convert 99123 in the first half of the expression to 1999-01-01. The second half of the equation adds days to the year based using the Mod command (remainder function). Thus, the mod of 99123 divided by 1000 is 123. It then adds 123 days to the beginning of the year from the first part of the equation, to give the correct date. If the source dates are already in the format of 1999123, then the 1900000 does not need to be added to the SDIVD field.
Convert Julian Date To Gregorian Date

Convert Lunar To Gregorian
Document Information
Convert Julian Date To Gregorian Oracle
Modified date:
15 June 2018
